Data lifecycle management (DLM) is the process of safeguarding data appropriately throughout its existence. The basic data lifecycle stages are creation, storage, data usage, sharing and destruction:
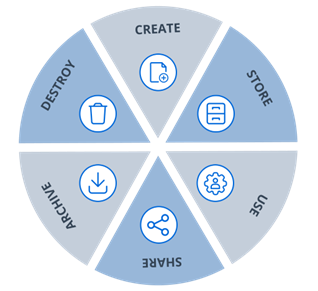
Figure 1. The 6 basic data lifecycle management stages
The goal of DLM is to ensure data security and regulatory compliance during all stages without throttling business productivity. Achieving this goal requires different processes and policies at various times during the data lifecycle. For example, most data protection strategies for stored digital content include a variety of access control measures.
Note that data lifecycle management is closely related to information lifecycle management (ILM), but there is a subtle difference between the two. DLM is concerned with raw data like files and databases, and their attributes, such as file type, size and age. ILM goes further to include the information in a file or database record and how different pieces of data are connected. For example, multiple pieces of raw data stored in different data silos might comprise a piece of information, such as a company’s purchase order. Both DLM and ILM can cover both structured and unstructured content, on premises or in the cloud.
Three Main Goals of Data Lifecycle Management
The most important data lifecycle management goals are the three components of the CIA Triad:
- Confidentiality — Data must be secured against unauthorized access, sharing and theft.
- Integrity — Data needs to be authentic, accurate and reliable. One threat to data integrity is having multiple versions of the same data and no clear indication of which is authoritative; effective data management is needed to prevent such sprawl.
- Availability — Since business runs on data, it’s crucial to ensure that it’s available to authorized users via search or other navigation methods. Availability also includes effective data processing and visualization to inform business strategy.
Phases of Data Lifecycle Management
The six basic phases of DLM illustrated earlier can be given more descriptive names, as follows:
- Create: Generate & Collect — Data can be created internally or collected by IT systems. For example, users both send and receive email messages, and their browsers often store cookies and search history details.
- Store: Process & Manage — After it’s created, data is stored in databases, file shares, data warehouses and so on. The data should be classified according to its sensitivity and value, including whether which regulations it is covered by, to guide data management and protection processes like access control, encryption and data loss prevention (DLP). It also might be classified as hot, warm or cold, depending on how frequently it is accessed.
- Use: Analyze & Visualize — A variety of stakeholders need to use the data, from business users to customers and partners. Often, data analysis and visualization is driven by enterprise resource planning (ERP), human resources (HR), customer relationship management (CRM) and related applications.
- Share: Share and Communicate — Users often need to provide data to others or to collaborate. DLM must ensure that sharing is limited to what’s necessary and permitted by internal policies and external regulations.
- Archive — Data that is no longer being used is typically archived to tape, disk or cloud storage. Archiving is valuable for data that cannot yet be destroyed due to business needs or regulatory requirements. Data can be archived in its original format or in another format, such as a dump or export, and is often encrypted.
- Destroy: Re-use & Repurpose or Destroy — Data that no longer being used and does not have be retained for policy reasons can be deleted. However, it is worth first asking whether the data can be re-used for some other purpose.
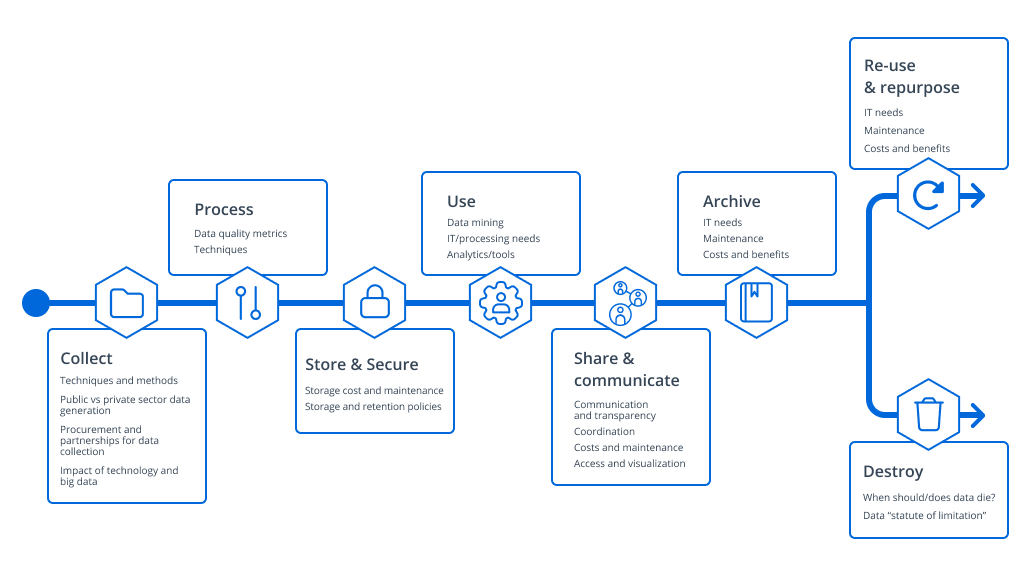
Figure 2. A detailed breakdown of the phases of data lifecycle management
How Netwrix Can Help
Organizations today often have petabytes of structured and unstructured data stored across many data silos, so effective DLM is simply not possible with manual methods. But the Netwrix Data Access Governance solution empowers you to easily to manage the entire data lifecycle from a single pane of glass.
In particular, this solution helps you prevent unauthorized access to your data by streamlining the work of granting, revoking, reviewing and monitoring access to your sensitive data. A range of reporting and analytics tools enable you to promptly identify security threats in their early stages, as well as to respond effectively with detailed information about how the incident occurred and what data was affected. In addition, you can quickly recover to a secure state and develop a more effective security strategy going forward.
FAQ
1. What is data lifecycle management (DLM)?
Data lifecycle management includes all of the processes, policies and procedures an organization uses to manage business data, from creation through destruction. DLM isn’t a specific product; rather, it’s a framework that ensures a comprehensive approach to data security.
2. What are the three main goals of data lifecycle management?
The three main goals of DLM are data confidentiality, data availability and data integrity. Confidentiality means data is protected from unauthorized access. Availability means data can be quickly accessed by authorized uses. Integrity means the data is accurate and consistent.
3. What are the stages of the data lifecycle?
The stages of the data lifecycle are: creation, storage, data usage, sharing and destruction
- Creation: Data is captured or generated.
- Storage: Data is stored, classified and processed.
- Use: Data is analyzed and visualized.
- Sharing: Data is communicated between users.
- Archival: Data that no longer active but needs to be preserved is moved to long-term storage.
- Destruction: Data that is no longer used and that doesn’t need to be preserved is deleted.


